Imagine that you are in the process of creating a product. If this is the case, developing a prototype of the product before beginning production on a large scale may prove to be extremely beneficial. In the same vein, CNC precision machining, also known as CNC milling and turning, offers a number of advantages when used in conjunction with the CNC rapid prototyping process. Keep in mind that CNC is short for computer numerical control. In this vein, we will provide an answer to a frequently asked question: how can plastic or metal prototypes be created using CNC machining? In addition to that, we will also talk about the advantages of using plastic and metal for prototyping. So, let's get started.
What are the steps involved in using CNC machining to create a prototype made of metal and plastic?
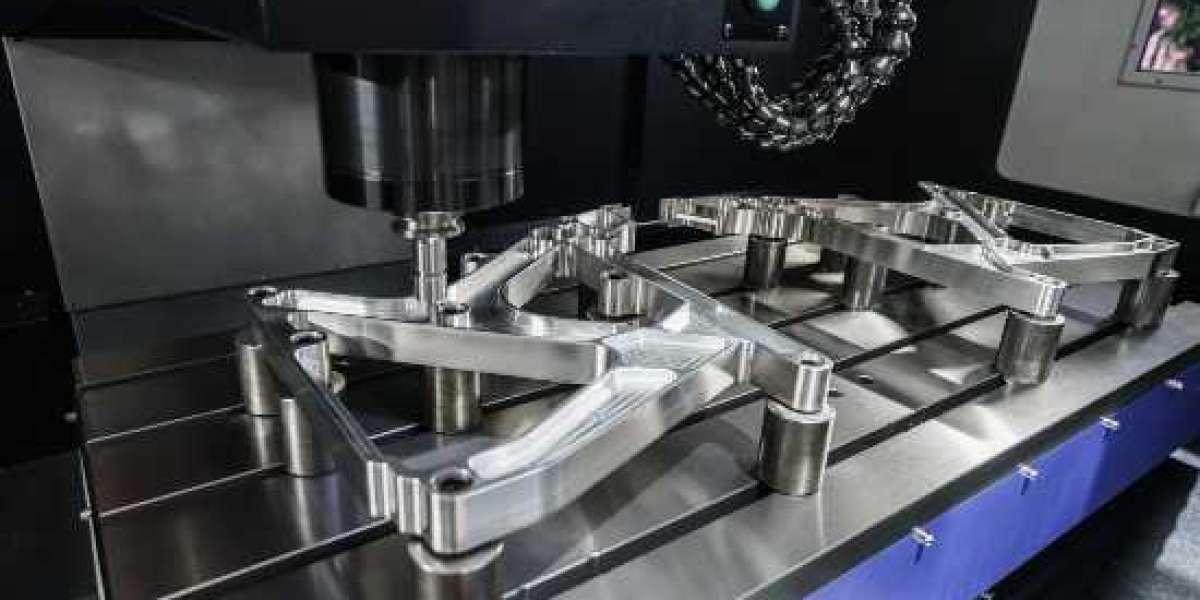
CNC machining has the potential to be the most efficient and effective method for creating metal and plastic prototypes, depending on the geometry of the part. Typically, CNC machines create three-dimensional objects by first starting with a solid block and then using cutting tools to remove excess material from the block. The series of cutter paths are directly generated from the 3D CAD model, which allows for extremely precise control over the movement of these tools. Computer-aided manufacturing software, also known as G-code, is another name for the software that is used to convert 3D CAD models into machine code. CAM is an abbreviation for computer-aided manufacturing.
At this point in time, CNC rapid prototyping has developed into a method that is widely used. It is extremely practicable and adaptable for a wide variety of product sizes across a comprehensive spectrum. Rapid prototyping or short-run production work can be accomplished with the help of the CNC process in many different industries, including but not limited to automotive, aerospace, healthcare, defense, electronics, and others.
Meanwhile, threaded and undercut features can be included in metal and plastic CNC rapid prototyping thanks to the technology's full potential. It lends itself especially well to the creation of prototypes, which typically call for precise tolerances, controlled sizes, and improved surface finishes. The surface finish of machined parts can be improved further through secondary processes such as polishing, painting, bead blasting, and plating. Machined parts are ready to be used immediately after processing.
The rapid turnaround time offered by CNC rapid prototyping assists industry professionals in validating all of the design fundamentals and parameters. For example, CNC machining makes it possible to evaluate the form, fit, and function of injection-molded parts without having to make an initial investment in mold tooling.
The process of prototyping in metal and plastic using computer numerical control machining.
The creation of the digital 3D design of the component, which is done with CAD/CAM software, is the first step in the CNC rapid prototyping process. When the design is complete, the CNC machine is given instructions regarding the process to follow in order to create the object. These pieces of information are represented by G-Codes and M-Codes respectively. Following the input of the codes into the CNC system, a subtractive process will begin. It indicates that some of the material from the metal or plastic block will be removed in order to bring it into the desired shape.
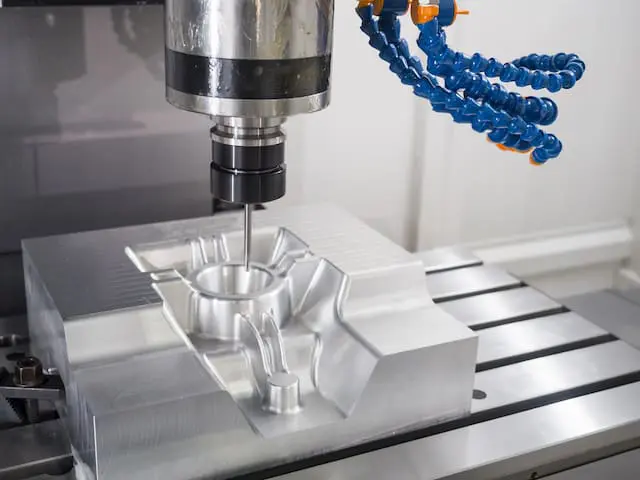

During the process of additive manufacturing, an object is formed by 3D printers by successively adding layers of material. In contrast, the process of subtractive manufacturing is referred to as CNC machining. It is composed of the cutting sections that slice away at the block of material in order to remove or dispose of excess material. CNC machines with a higher level of complexity are able to work with multiple axes (3-5axis) and different tool-sets. As a result, it is now possible to cut the workpiece using significantly more complicated methods and intricate geometries. It contributes to an increase in both the productivity and the speed of production.
Common Materials Employed in the Prototyping of Metal and Plastic Products
The following types of materials are typically utilized when plastic prototypes are created using CNC machines:The material is polycarbonate. ABS, Acrylic/PMMA, PP, Nylon, Teflon, and Acetal/POM are the six different types of plastics. On the other hand, prototyping in metal using CNC machining may also use a variety of other materials. Generally speaking, these will consist of Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium, Titanium, Brass, and Copper.
There is a wide variety of standard plastic grades that are simple to machine. As an illustration, ABS is a low-cost material that is both versatile and truly machinable. However, PP and POM are more difficult to cut and more likely to distort after being cut. In a similar vein, the machinability of metallic materials can vary greatly depending on the type. Aluminum is likely to be a delicate metal that is also soft, easy to cut, and quick to machine. Steel, on the other hand, is an extremely durable material.
In accordance with the specifications, CNC rapid prototyping can be performed with any of these materials. It is imperative that the surface finishing and overall quality of the prototype not be compromised in any way. Keep this in mind. Nevertheless, the manner in which the process is carried out is very important. This is also defined by the quality of the CNC machine and tools that are used in the prototyping process.